Urinary Tract Infection(UTI): Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Urinary Tract Infection(UTI): Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
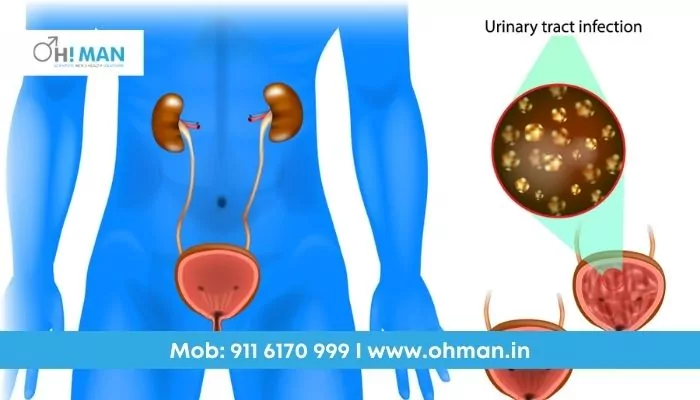
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is an infection caused by bacteria, fungi or other microbes in the human urinary system. The Human Urinary system includes the urethra, ureters, bladder and kidneys. Symptoms of UTIs include the urge to urinate often, pain during urination or irritation and burning. However, UTIs are easily treated with the use of antibiotics.
- What is Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
- What is Urinary Tract?
- Who is prone to UTIs?
- How Common are urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
- Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infection
- Causes Of Urinary Tract Infection
- Difference between Urinary Tract Infection & Chlamydia
- Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections
- Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
- Complications of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
- After Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
An infection of the urinary tract (UTI) can be described as an infection that affects the urinary tract. The type of infection could be a problem with your:
- urinary tract (a condition known as urethritis)
- kidneys (a condition known as the pyelonephritis)
- the bladder (a condition known as cystitis).
Urinary tract infections are extremely frequent, occurring in one out of five women throughout their lives.
While UTIs are more common among women, they also occur in men, older adults, and children. A small percentage of children suffer from Urinary tract infections. Every year, between 8 and 10 million visits to the doctor are due to urinary tract infections.
The urine doesn’t contain microbes (germs). Urine is a product of the kidneys’ filtration system, and urine forms when excess water eliminates from your blood through your kidneys.
Typically, urine travels through your urinary system without any contamination. However, there are times when bacteria may get into your urinary system through the outside. So this causes problems such as inflammation and infection.
What is Urinary Tract?
The urinary tract produces and stores urine, one of the bodily’s fluid waste products. The urinary tract comprises the following elements:
- Kidneys are small organs located behind your back, right above your hips. They function as your body’s filter, removing water and waste from your blood—the urine results from this waste.
- Ureters are thin tubes that transport urine from your kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-shaped organ that stores urine before it leaves the body.
- Urethra This tube transports the urine out of your bladder to the outside of your body.
Who is Prone to UTIs?
Anybody can suffer from an infection of the urinary tract. However, UTIs are more prevalent in females. This is because the urinary tract (the tube that transports urine out of the body) in females is narrower and is closer to the anus. This is the place where E. coli bacteria are prevalent. The older age group is also more likely to develop cystitis.
Further, the incomplete discharge of the bladder causes this higher risk. There are a variety of medical conditions associated with this, like an enlarged prostate or prostate prolapse (a condition in which the bladder slips from its normal position).
Suppose you experience frequently recurring urinary tract infections or urine infections. Your physician may perform tests to determine if you have other health issues — for instance, diabetic issues or an unbalanced urinary tract — contributing to the UTIs.
Additionally, people who have frequent UTIs are often prescribed low-dose antibiotics over a long period to stop the infection from returning.
Further, this method of treating frequent UTIs is because the body could develop resistance to the antibiotic, and you may develop other forms of infections, like C. diff colitis. However, this practice is quite often.

How Common are urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are widespread in women; 1 out of 5 women suffer from UTIs at some time in their life. However, UTIs also infect men, children & older adults.
Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections rarely create symptoms and signs; however, when they do, they can be accompanied by:
- An intense, constant urge to pee or urinary incontinence
- An intense burning sensation during urination.
- Small amounts of urine
- The color of the urine can be cloudy.
- Urine that is bright pink, bright red, or cola-colored indicates blood present in your urine.
- Urine that smells strong
- Pelvic pain in women, particularly around the pelvis and in the pubic bone
UTIs can be mistaken or missed for other ailments when older adults are diagnosed with a condition.
Some other symptoms UTIs can show are:
- Pain during sex.
- Pain inside Penis.
- Discomfort or lower back pain
- Fatigue.
- Fever (temperature above 100 degrees Fahrenheit) and chills.
- Vomiting
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections usually occur when bacteria infiltrate the urinary tract via the urinary tract and begin to multiply within the bladder. Though the urinary tract is designed to block microbes that invade the urinary tract, these defenses can fail. If this happens, bacteria could take hold and cause a full-blown infection of your urinary tract.
The most well-known UTIs are more common in women and can affect the bladder and the urethra.
- Infection of the bladder (cystitis). This kind of UTI usually results from is usually caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli), a strain of bacteria commonly found in the digestive (GI) tract. But, occasionally, other bacteria may be involved.
- Sexual activity can cause cystitis. However, it doesn’t require you to be sexually active to get it. Women of all ages are susceptible to developing cystitis due to the shape of their anatomy, specifically, the small distance from the urethra’s opening to the anus and the urethral opening that connects to the bladder.
- Infection of the urinary tract (urethritis). This UTI could occur if GI bacteria are spread through the anus and into the urethra. Furthermore, because the female urethra is close to the vagina, sexually transmitted diseases can lead to urethritis. The infections can be chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, and mycoplasma.
Difference between Urinary Tract Infection & Chlamydia
Chlamydia is an infection transmitted by sexual contact (STI) caused due to the bacteria Chlamydia Trachomatis. It quickly spreads through sexual fluids such as pre-cum, semen, and vaginal fluids. Further, it can also affect any part of the genitals, anus, throat, and eyes.
While a series can quickly treat the condition antibiotics, the Chlamydia bacteria typically do not show any signs until the disease has progressed into more advanced stages. Be aware that chlamydia may return after treatment if you are infected.
- Common symptoms you could notice are:
- Urinary pain or having sexual relations
- Genital discharge
- Pain in the testicle
- Bleeding during periods or after sexual activity
If you’re experiencing symptoms similar to these, you should consider the possibility of testing for infection.
It is crucial not to let a chlamydia-related infection remain untreated as you could be at risk of developing more severe health problems. For instance, the long-term consequences of chlamydia can result in grave issues in the reproductive system, which may cause infertility.
But why do people confuse urinary tract infection and chlamydia?
A notable characteristic of chlamydia and UTIs are the symptoms they experience when they urinate. Also, both chlamydial infections and urinary tract infections can lead to burning or pain while you urinate and regular or painful the process of urination. Moreover, chlamydia and urinary tract infections can cause discomfort within the abdomen or the pelvic region.
Additionally, the most prominent characteristic that chlamydia doesn’t have in common with UTIs is vaginal or penile discharge. Chlamydial infections can trigger an unpleasant, yellow-colored vaginal discharge or a watery lacy penile discharge.
Further, urinary tract infection men or in women doesn’t cause any abnormal discharge from the genitalia.

Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections
Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections involves various stages of diagnosis, starting from testing urine samples in the lab. Taking images of the urinary tract through MRI and CT Scan. After these steps, the doctor thinks that he needs more evidence or to find the correct data on infection, then he can suggest a cystoscopy to check the entire Urinary tract.
Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
There is a need to treat urinary tract infections. Antibiotics are medications that destroy bacteria and fight infection. Further, your doctor will recommend the best antibiotic to treat the particular bacteria responsible for your condition. Commonly used antibiotics include:
- Nitrofurantoin.
- Sulfonamides (sulfa drugs).
- Cephalosporins.
- Amoxicillin.
- Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim(r)).
- Doxycycline.
- Quinolones (such as Ciprofloxacin [Cipro(r)].
It’s crucial to adhere to your doctor’s instructions regarding the medication dosage. Do not stop taking the antibiotic since your symptoms will go away, and you will begin to feel better. It may return if the infection doesn’t go away with complete treatment.
Suppose you’ve had a long-standing previous history of frequent urinary tract infections. In that case, the doctor may prescribe you antibiotics you should begin taking when you first notice the beginning of symptoms.
Additionally, others may receive antibiotics that they take daily or every other day or following sexual activity to avoid the infection. Discuss with your doctor the best UTI treatment for you in the event of a previous history of frequent UTIs.
Complications of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) mostly involved antibiotics. However, problems start when you do not complete your medicine or stop medication halfway through your treatment. Then you face frequent infections in your Urinary Tract despite taking medicines. If this situation is left untreated, infection can reach the kidneys.
After Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
The symptoms of UTIs typically improve within just a few days after taking antibiotics. If the UTI symptoms have gone away following the completion of your course of treatment, you don’t require a second urine test to confirm that the infection is all gone.
Based on the circumstances, if you’re suffering from a highly complicated UTI, you will likely require the results of a urine test to confirm how the UTI is gone. However, if the symptoms don’t disappear even after taking antibiotics, you might need a different antibiotic, a different type of antibiotic, or an alternative method to take it.
Infections of the urinary tract can be painful, but you can take steps to alleviate discomfort until antibiotics can treat the infection.
Take these steps:
- Drink plenty of water. Water helps to dilute urine and eliminate bacteria.
- Avoid drinking Substances that could irritate your urinary tract. Avoid coffee, alcohol, and soft drinks that contain caffeine or citrus juices until the infection has gone away. They can irritate your bladder and aggravate your frequent or pressing urge to go to the bathroom.
- Utilize a heating pad. Apply a warm but not hot heating pad to your abdomen to reduce the pressure on your bladder or cause discomfort.
Conclusion
Contact your doctor if you are experiencing some of these signs or if your other symptoms persist following treatment. UTIs are serious conditions that can cause a lot of discomfort, and UTIs can spread all over your urinary tract and other areas in your body. However, treatment for UTIs is effective and can speedily relieve the symptoms. Have doubts about UTIs? Visit Ohman Consult to our experts and clear your all doubts today. Ohman is men Sexual health platform that provide FDA-approved best Medicine for Penis Enlargement in India and Dhat ki dawa as well as trying to educate the world about the men sexual health problem.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Will a UTI cause damage to the kidneys?
Ans – It’s rare. In most instances, UTI treatment is successfully possible without causing damage to the kidneys. UTIs caused by conditions such as a large prostate gland (in males) or kidney stones can cause kidney damage when the issue isn’t treated and the infection persists. - Why do I get UTIs?
Ans – UTI can result from a UTI may occur by letting bacteria get into the urethra, and this is the tube urine flows through before exiting the body. The bacteria can enter the urethra in several ways, such as by sexual contact, inadequate hygiene, or an existing bladder problem. - When should I be worried about UTIs?
Ans – If you’re treated for UTI and aren’t showing any signs of improvement or are suffering from symptoms of UTI as well as stomach upset and vomiting or having chills and fever, you must consult your physician. If you notice the presence of blood within your urine, consult your physician immediately. - Is it possible to become immune to the antibiotics used to treat a UTI?
Ans – Yes, and you may develop an antibiotic-resistant UTI. Further, the antibiotic-resistant UTI may develop into an ongoing condition that can often trigger frequent episodes of infection, resulting in the risk of developing serious kidney infections (pyelonephritis) or even sepsis. - Does cranberry juice help prevent urinary tract infection (UTI)?
Ans – Many people believe that cranberry juice may aid in the treatment of or help prevent UTIs. Researchers are currently studying the issue but haven’t come up with any definitive answers yet. Drinking unsweetened cranberry juice isn’t an established method to avoid the occurrence of a UTI However, it will not harm you in any way.



